You’re wandering through the corridors of your favorite video game, awestruck by the lifelike environments and characters. Or you’re watching the latest blockbuster movie with jaw-dropping special effects. Ever wondered how those visuals come to life? Enter the fascinating world of 3D rendering. It’s like the fairy godmother of digital visuals, transforming simple models into complex, stunning images that make us go, “Wow!”
The Basics of 3D Rendering
At its core, 3D rendering is the process of converting 3D models into 2D images on your screen. Think of it like baking a cake. You start with raw ingredients (3D models) and through a series of magical transformations (the rendering process), you end up with a deliciously detailed image. The aim is to produce images that are as realistic or stylized as the creator desires.
How Does 3D Rendering Work?

Imagine you’re an artist with a blank canvas. You begin with basic shapes or models, adjust lighting, textures, and colors, and finally render the scene to bring it to life. In technical terms, rendering is a process that involves complex algorithms and mathematical calculations. It takes into account numerous factors such as light sources, reflections, shadows, and textures to create a realistic image.
Types of 3D Rendering
There are several methods to achieve 3D rendering, each with its unique flair and application. Let’s take a quick tour:
- Real-Time Rendering: This method is often used in video games and interactive graphics. It aims for speed and efficiency, allowing users to interact with the scene in real-time. The visuals may not be as polished as other methods, but the ability to interact with the environment without delay is a game-changer.
- Offline Rendering: Known for its high-quality results, offline rendering is used in films and detailed architectural visualization. It doesn’t have the constraints of real-time, allowing for more detailed and photorealistic images. However, the trade-off is time, as rendering can take hours or even days for a single frame!
- Ray Tracing: This technique simulates the way light interacts with objects, creating stunningly realistic images. It’s like giving your digital world a touch of Mother Nature’s brilliance. Though computationally intensive, advancements in technology have made ray tracing more accessible.
The Tools of the Trade
Like any artist, a 3D renderer needs the right tools. Software such as Blender, 3ds Max, and Maya are popular choices among professionals. These tools offer a range of functionalities, from modeling and texturing to animation and rendering. For those who prefer a more hands-off approach, there are numerous 3D models available online to kickstart your project.
Hardware Considerations
Rendering is a resource-intensive task, often requiring powerful hardware to handle the workload. Graphics cards, or GPUs, are the unsung heroes here, processing complex calculations and delivering those breathtaking visuals. With the advent of cloud computing, even small studios can access powerful rendering capabilities without breaking the bank.
Theoretical Insights: Lighting, Textures, and More
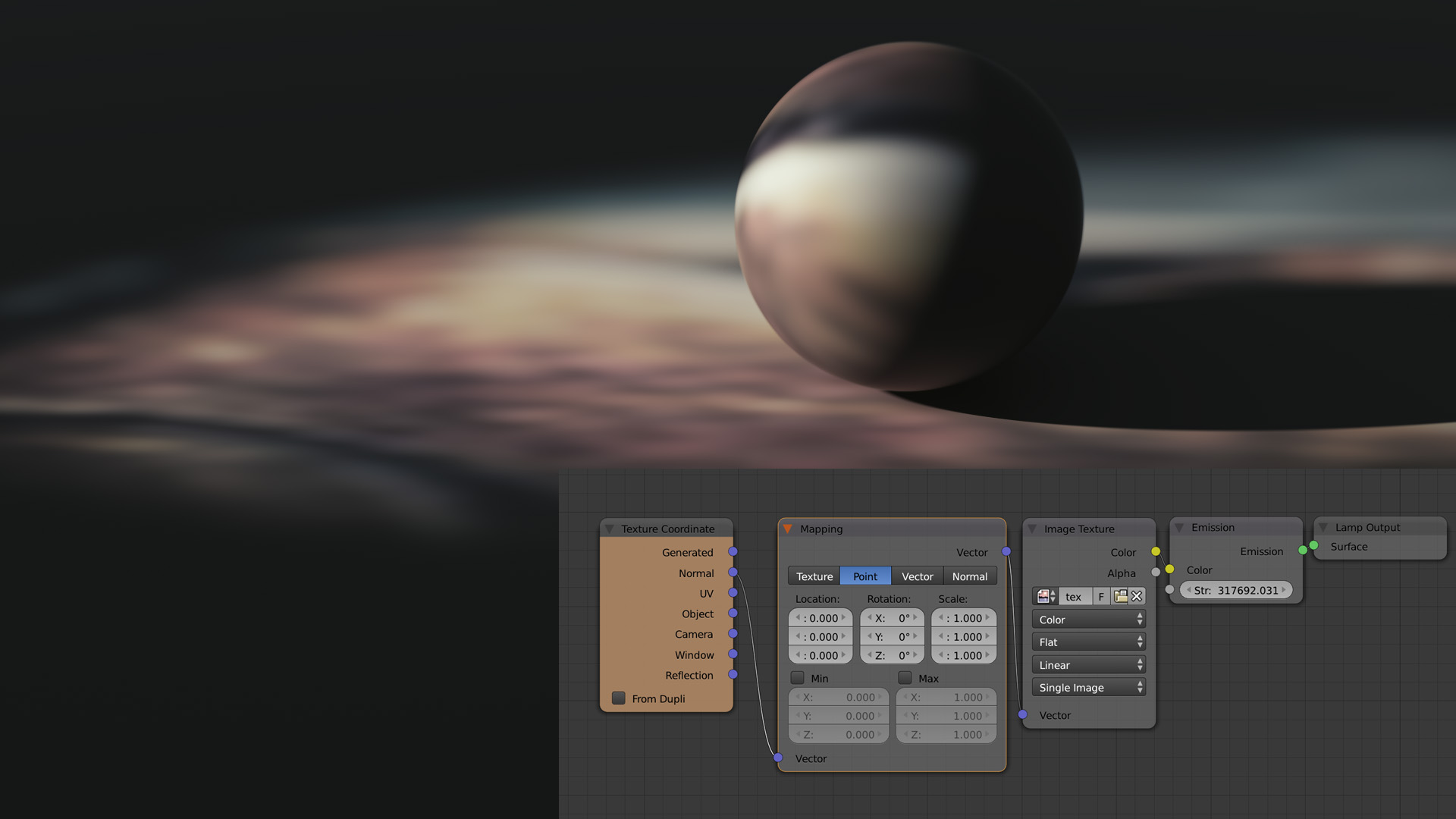
Let’s dive a bit deeper into the theoretical aspects of 3D rendering. At the heart of creating realistic images are three crucial components: lighting, textures, and shading.
Lighting
The play of light and shadow can make or break a scene. In the world of 3D rendering, lighting is an art form in itself. Artists meticulously position virtual light sources to simulate natural lighting conditions, creating depth and atmosphere. Whether it’s the warm glow of a sunset or the eerie ambiance of a moonlit night, lighting sets the mood and tone of the scene.
Textures
Textures give surfaces their feel and appearance, turning a flat object into, say, a rough stone wall or a shiny metal surface. Textures are like the icing on the cake, adding realism and detail to the models. Artists use various techniques to map textures onto 3D models, ensuring they blend seamlessly with the lighting and environment.
Shading
Shading is the process of defining how surfaces interact with light. It determines how light scatters, reflects, and refracts on a surface, playing a crucial role in achieving realism. Different shading models, such as Phong or Blinn-Phong, offer varied approaches to how light behaves, giving artists flexibility in achieving their desired look.
The Impact of 3D Rendering on Various Industries
3D rendering is not just for games and movies. Its impact spans numerous industries, revolutionizing the way we create and interact with digital content.
Architecture and Interior Design
Gone are the days of flat blueprints. Architects and designers now use 3D rendering to create immersive visualizations of their projects. Clients can take virtual tours of buildings before a single brick is laid, making it easier to visualize and tweak designs.
Automotive and Product Design
From car manufacturers to gadget designers, 3D rendering helps visualize complex designs before production. It allows designers to experiment with different materials, colors, and features without the cost of physical prototypes.
Marketing and Advertising
3D rendering has opened new doors in the world of marketing. Stunning visuals and animations can showcase products in their best light, attracting customers and boosting sales. It’s like having a virtual salesperson always ready to impress!
Challenges and Future Prospects

Despite its many advantages, 3D rendering is not without challenges. The demand for high-quality visuals continues to push the boundaries of technology and creativity. Artists and developers strive to find the balance between quality and efficiency, especially in real-time applications.
Looking ahead, the future of 3D rendering is bright. With advancements in AI, machine learning, and hardware capabilities, the possibilities are endless. Imagine a world where rendering is instantaneous, and the line between virtual and reality is blurred.
So, the next time you’re mesmerized by a stunning visual in a game or movie, think of the complex and fascinating world of 3D rendering that made it possible. And remember, it’s not just the technology but the creativity of artists and developers that brings these digital dreams to life.