3D scanning technology has fundamentally changed many industries by providing detailed three-dimensional models for a variety of applications. However, for beginners, understanding this sophisticated technology can be challenging. This article aims to demystify 3D scanning and provide an accessible guide for beginners.
What is 3D Scanning?
3D scanning is a non-contact, non-destructive technology that digitally captures the shape of physical objects using a line of laser light (https://www.lmi3d.com/what-3d-scanning). 3D scanners create “point clouds” of data from the surface of an object. In essence, these point clouds are used to generate a 3D representation of the scanned object, providing incredible levels of detail and accuracy.
Understanding the Technology Behind 3D Scanning
3D scanners employ a variety of technologies to capture data, including laser triangulation, structured light, time-of-flight, and photogrammetry. Each technology has its strengths and weaknesses, making them more or less suited to different types of scanning projects. For instance, time-of-flight scanners are excellent for large objects and spaces, while structured light and laser triangulation scanners excel at capturing small, detailed items.
How Does 3D Scanning Work?
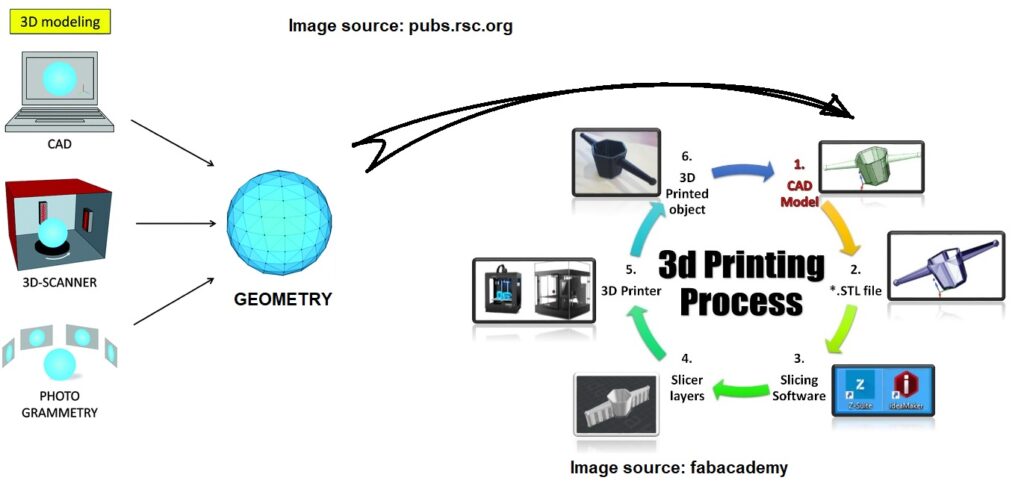
3D scanning comprises three key steps:
- Data Acquisition: The 3D scanner captures the geometry of the object by taking multiple snapshots from different angles. Each snapshot generates a ‘point cloud’ that represents the object’s surface in 3D space.
- Point Cloud Processing: This is where the individual point clouds from various snapshots are aligned and merged into a single 3D model.
- Post-Processing: Depending on the intended use, the final 3D model may be cleaned up, optimized, or otherwise manipulated in software such as MeshLab or Autodesk’s ReCap before it’s ready for use.
Types of 3D Scanners
There are various types of 3D scanners available, each with its pros and cons. The most commonly used are:
| Scanner Type | Ideal Use Cases | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Laser 3D Scanners | Industrial design, Manufacturing, Quality control | Faro’s Laser Scanners |
| Structured Light Scanners | Cultural preservation, CGI, Healthcare | Artec 3D’s Eva |
| Photogrammetry | Game development, Virtual reality | Agisoft Metashape |
Getting Started with 3D Scanning
Jumping into 3D scanning can seem daunting, but many resources are available to help you get started. For beginners, companies like Matterport provide easy-to-use hardware and software that can help you create high-quality 3D scans. In addition, online communities, such as the 3D Scanning Users Group on Facebook, are great places to learn from and connect with other enthusiasts.
Applications of 3D Scanning
3D scanning has wide-ranging applications across multiple industries. Some of the key uses are:
- Manufacturing: For quality control, reverse engineering, and rapid prototyping.
- Entertainment: In CGI for movies and video games for creating realistic models.
- Healthcare: For creating custom prosthetics, implants, and for surgical planning (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5990432/).
- Architecture: For building inspections and creating accurate BIM models.
- Archaeology: For preserving and studying historical and cultural artifacts.
The Future of 3D Scanning
The future of 3D scanning is bright, with advancements continually pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As technology improves, we can expect higher resolution scanners, faster processing times, and even more applications. In addition, the convergence of 3D scanning with other technologies such as VR and AR opens up exciting new possibilities for interaction with the digital world (https://www.forbes.com/sites/charliefink/2018/01/19/ces_report_ar_and_vr_trending_up/?sh=5a1c708c6527).
Conclusion
3D scanning has revolutionized the way we perceive and interact with the physical world. As a beginner, understanding this technology opens doors to countless opportunities. Whether you’re in manufacturing, healthcare, entertainment, or archaeology, 3D scanning has something to offer.
For those interested in going further into this exciting world, resources like 3D Scan Expert and Aniwaa’s guide to 3D Scanning provide invaluable information.
Please provide me with more details on the topic
It’s the best time to make some plans for the future and
it is time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could
I wish to suggest you few interesting things or advice. Maybe you can write next
articles referring to this article. I desire to read even more things about it!